Birdwatching Mastery Blog
Explore the world of birdwatching with tips, guides, and inspiration.
Ears Don’t Lie: The Surprising Truth About Sound Quality You Never Knew
Uncover the hidden secrets of sound quality! Discover why ears don’t lie and learn the surprising truths that will change your listening experience!
The Science Behind Sound: How Quality Impacts Your Listening Experience
The science behind sound is a fascinating intersection of physics, biology, and technology, all of which converge to shape our auditory experiences. Sound waves, which are vibrations that travel through air or other mediums, provoke various reactions in the human brain. The quality of these sound waves is crucial; it influences not just the clarity of what we hear, but also our emotional and psychological responses. For instance, high-quality audio systems can reproduce sound with greater fidelity, leading to a more immersive listening experience. When every note is crisp, and every beat is felt, our overall enjoyment increases significantly.
Furthermore, quality plays a pivotal role in how sound is perceived and interpreted. Advanced technologies such as noise-cancellation and high-definition audio aim to enhance this experience. Research indicates that environments with fewer distractions allow our brains to process sound more efficiently, making us more aware of nuances in music or dialogue. As a result, the impact of context, along with the technological quality of sound, can profoundly alter how we engage with auditory content. When investing in sound equipment or experiencing audio in various settings, it is essential to understand these factors for an optimal listening experience.
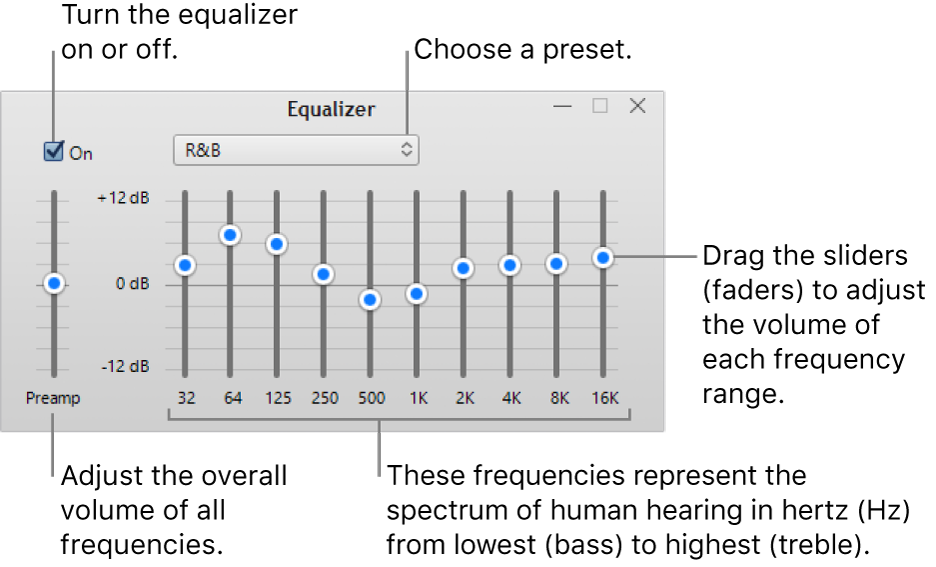
Counter-Strike is a popular first-person shooter game that pits teams of terrorists against counter-terrorists in various objective-based rounds. Players can choose from a variety of weapons and strategies to outsmart their opponents. If you're looking for audio gear to enhance your gaming experience, check out the Top 10 Earbuds for Small Ears.
Are You Hearing What You Think You’re Hearing? Debunking Sound Quality Myths
When it comes to sound quality, misconceptions abound that can influence how we perceive audio. One of the most prevalent myths is that higher price always equals better sound. While it’s true that premium audio equipment often offers advanced technology and superior build quality, sound quality is a subjective experience affected by numerous factors, such as individual hearing ability and acoustic environment. In fact, many budget-friendly options can deliver remarkable audio performance, challenging the idea that costly gear is always the best choice.
Another common belief is that specific formats, like lossless audio, are always superior. While lossless formats retain more data, the real difference in sound quality often depends on the listener's setup and personal preferences. For instance, in casual listening environments, many listeners may not notice much of a difference between a high-quality compressed file and a lossless version. Understanding these nuances helps debunk the myth that more expensive or tech-heavy solutions are necessary for an enjoyable auditory experience.
The Hidden Factors Affecting Sound Quality: What You Need to Know
When it comes to sound quality, several hidden factors can significantly influence your listening experience. Firstly, the room acoustics play a crucial role; sound waves interact with each surface, leading to reflections, reverberations, and dead spots. For instance, hard surfaces like glass and concrete can create harsh echoes, while soft furnishings like curtains and carpets help absorb sound, leading to a more balanced audio environment. Understanding room treatment options—such as acoustic panels and bass traps—can help you optimize the space for better sound quality.
Another pivotal element affecting sound quality is the source material that you are listening to. High-resolution audio files provide a richer sound experience compared to lower quality formats, due to their greater depth and dynamic range. Additionally, the equipment used, from speakers to amplifiers, can introduce variances that either enhance or detract from the original sound. It's essential to consider not only the quality of the music files but also the compatibility of your equipment to ensure you are getting the best possible output.